在阅读代码时候看到这个片段.
example = dataset_utils.image_to_tfexample(
image_data, b'jpg', height, width, class_id)
tfrecord_writer.write(example.SerializeToString())内部实现是这样的.
def image_to_tfexample(image_data, image_format, height, width, class_id):
return tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/encoded': bytes_feature(image_data),
'image/format': bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/class/label': int64_feature(class_id),
'image/height': int64_feature(height),
'image/width': int64_feature(width),
}))这里涉及的知识点有这些.
- tf.train.BytesList / tf.train.Int64List / tf.train.FloatList
- tf.train.Feature / tf.train.Features
- tf.train.Example
首先是第一类,他总共三个,分别处理不同数据.
import tensorflow as tf
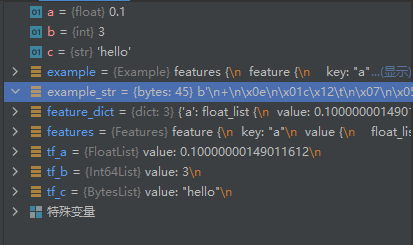
a = 0.1
b = 3
c = "hello"
tf_a = tf.train.FloatList(value=[a])
tf_b = tf.train.Int64List(value=[b])
tf_c = tf.train.BytesList(value=[bytes(c, encoding='utf-8')])
print([tf_a, tf_b, tf_c])输出内容.
[value: 0.10000000149011612
, value: 3
, value: "hello"
]通过Feature做Features,代码如下.
feature_dict = {
"a": tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf_a),
"b": tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf_b),
"c": tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf_c)
}
features = tf.train.Features(feature=feature_dict)
print(features)结果:
feature {
key: "a"
value {
float_list {
value: 0.10000000149011612
}
}
}
feature {
key: "b"
value {
int64_list {
value: 3
}
}
}
feature {
key: "c"
value {
bytes_list {
value: "hello"
}
}
}最后引出主角Example方法,通常为了储存,都会序列化他.
example = tf.train.Example(features=features)
example_str = example.SerializeToString()结果当然是一串byte.
还原方法就是用FromString,逐步还原,不过这个就是pb格式文件,如果按照特定格式做也就是TFRecord.